A septic tank is an underground, water-tight container that collects and treats wastewater when your house is far from a city sewer system. Wastewater enters a septic tank and undergoes a settling process, with solid matter sinking to the bottom as sludge and oils float to the top as scum. For more information, click the link https://www.septictankarmadale.com.au/ provided to proceed.
Inlet and Outlet Tees
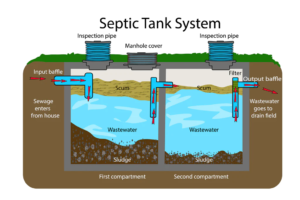
A septic tank is an underground, watertight container constructed to receive wastewater from homes and businesses. It is designed to hold the wastewater for a period of time, separate the solid waste from the liquid waste, cause reduction and decomposition of the accumulated solids, and to discharge the clarified water (effluent) from the septic tank to the absorption field.
A key part of the septic system is the inlet and outlet pipes. These pipes carry the wastewater from your home to and from the septic tank. The inlet pipe is a critical element because it helps to prevent sludge from entering the house sewer line, preventing clogs and overflows.
The inlet baffle (also known as a septic tank inlet tee) is located in the inlet pipe and serves several purposes. It slows the flow of wastewater and keeps it from stirring up the sludge layer inside the tank. In addition, it prevents odorous gasses from entering the home from the sewer line. The inlet baffle is a required component of the septic tank, per TCEQ regulations.
An important consideration when installing a new inlet baffle is the type of house sewer pipe it replaces. Older pipe often made of cast iron corrodes and can clog the inlet baffle. Most modern septic tanks use PVC sanitary tees in the inlet and outlet piping that are resistant to corrosion and do not clog.
As the septic tank fills with wastewater, a sludge and scum layer forms in the bottom of the tank. The inlet baffles help to maintain a level that allows the sludge and scum waste to settle before reaching the outlet pipe. The inlet baffle also helps to keep sludge and scum from flowing directly into the outlet pipe, causing drainfield clogs and premature system failure.
The outlet baffle, similar to the inlet baffle, must be in place and functional to allow the septic tank to function properly. It prevents the sludge and scum from traveling straight to the drainfield, causing clogs in the soil treatment system and premature system failure. Outlet baffles are often made from a PVC sanitary tee with an effluent filter that is designed to trap larger solids.
Pumps
There are many different pumps that can be used to pump septic tanks, and each has its own application. The pump that you use depends on the size of the tank and what you’ll be pumping from it. You also need to consider the particle size that the pump can handle, as you’ll want to make sure that the pump can safely move solid waste particles without clogging up your septic system or drain field.
As wastewater flows into your septic tank, solid waste settles at the bottom and lighter materials float to the top. Over time, these solids accumulate and reduce the amount of space available for new wastewater to enter. Pumping your septic tank regularly removes these solids, minimizing the risk of septic system failure and costly repairs.
Pumping your septic tank also prevents the solids from contaminating the environment. If these solids leak into the groundwater, they may pollute local water sources and create health hazards. If sewage overflows onto the property, it may create unpleasant odors and cause sewage backups inside your home.
Regular septic tank pumping also promotes proper functioning of your home’s drains. When sludge overload obstructs the flow of wastewater, toilets gurgle and tubs back up, resulting in unpleasant and expensive plumbing problems. Maintaining free-flowing drains throughout your house can save you from having to replace costly fixtures.
A properly maintained septic tank can also increase the value of your property. Potential buyers may be concerned about the condition of your sewer system, and a clean septic tank will reassure them that the home is well-maintained.
If you’re not sure whether your septic tank needs to be pumped, you can do a simple test at home. With the septic tank lid open, lower a septic tank gauge stick down into the tank (even through the thick sludge) until it hits the bottom and read the measurement on the gauge. This will help you estimate when the septic tank should be pumped, but it is best to have the septic tank pumped before it reaches 1 foot of sludge.
Absorption Fields
After primary treatment in the septic tank, liquid wastewater (effluent) travels to the absorption field. In this underground system, further bacterial action and soil acts as a physical, chemical and biological filter to purify the effluent before it is returned to groundwater. The soil also destroys pathogenic organisms that could contaminate drinking water and natural water resources. It is critical that the septic system be located in uncompacted, unsaturated soil.
The septic tank must be large enough to allow solid waste to decompose for at least 48 hours. This will reduce the volume of sludge and scum and keep the effluent from leaving the septic tank too quickly. A tee at the tank inlet slows the incoming wastes to prevent disturbing the sludge layer and a baffle at the outlet prevents solids from entering the soil absorption system. Tanks may have one or two compartments; research suggests that two-compartment tanks do a better job of separating solids and are required in some areas. All tanks should have accessible covers for checking the condition of the baffles and for pumping both compartments.
A septic system that is not properly maintained will send solids directly to the drainfield and clog it, requiring expensive repairs or replacement. In addition, contaminated effluent can contaminate groundwater and surface water. To minimize problems, an inspection is recommended at least every 2 to 5 years.
The drainfield consists of long underground perforated pipes that carry the liquid wastewater to the soil for final treatment. The soil acts as a filter to remove disease-causing bacteria, viruses and excessive nutrients from the wastewater before it is returned to groundwater. The drainfield can be arranged in trenches or beds. Trenches work best on sites with 5 percent or less slope, and beds are more suitable for sloping sites where space is limited.
A good sign that a septic system is not working correctly is lush green grass over the absorption field, even in dry weather. Another warning sign is a pungent odor near the septic tank, pump chamber or drainfield. A septic system inspector will be able to determine the cause of this odor and recommend an appropriate solution.
Maintenance
A septic tank is an alternative to connecting a home to the public sewer system. These systems work well for most households, but can be a nightmare when they aren’t properly maintained. Proper maintenance will extend a septic tank’s useful life and minimize the risk of environmental contamination.
All drain pipes from sinks, tubs and toilets lead to the septic tank. On the inlet side, a baffle regulates how much waste enters the tank at one time. Waste then separates into three main parts: solids at the bottom, liquids in the middle and a float layer of grease and oils at the top. Bacteria in the tank breaks down the solids. The liquid wastewater, called effluent, flows out through the outlet tee opening.
The liquid effluent flows out into the absorption field, where it travels through perforated pipes and seeps into the soil. This reprocesses the wastewater and lowers its toxicity. It also provides nutrients for plants, which absorb the waste and return clean water to the absorption field.
Maintaining proper septic system function is essential to keeping your family healthy and the environment safe. If the system isn’t maintained, waste could leak into the ground, contaminating soil and waterways. In addition, improperly maintained septic systems can create foul odors in the house.
The most important maintenance task is getting the septic tank pumped regularly. Typically, it should be pumped if the solids reach 25 to 33 percent of the tank’s liquid capacity.
It’s also a good idea to have the system inspected and cleaned every two to five years. Professionals will look for any signs of problems and inspect the drain field and pump system.
Parking vehicles or placing excessive weight above a septic tank or leach field can cause stress that eventually leads to cracking and failure of the system. It’s best to keep vehicles and large gatherings away from these areas.
It’s a good idea to save any maintenance records and have them available for potential buyers when selling a property with a septic tank. This information can reassure potential buyers and make them more likely to purchase a property.